Let X Continuous Random Variable With - Summary
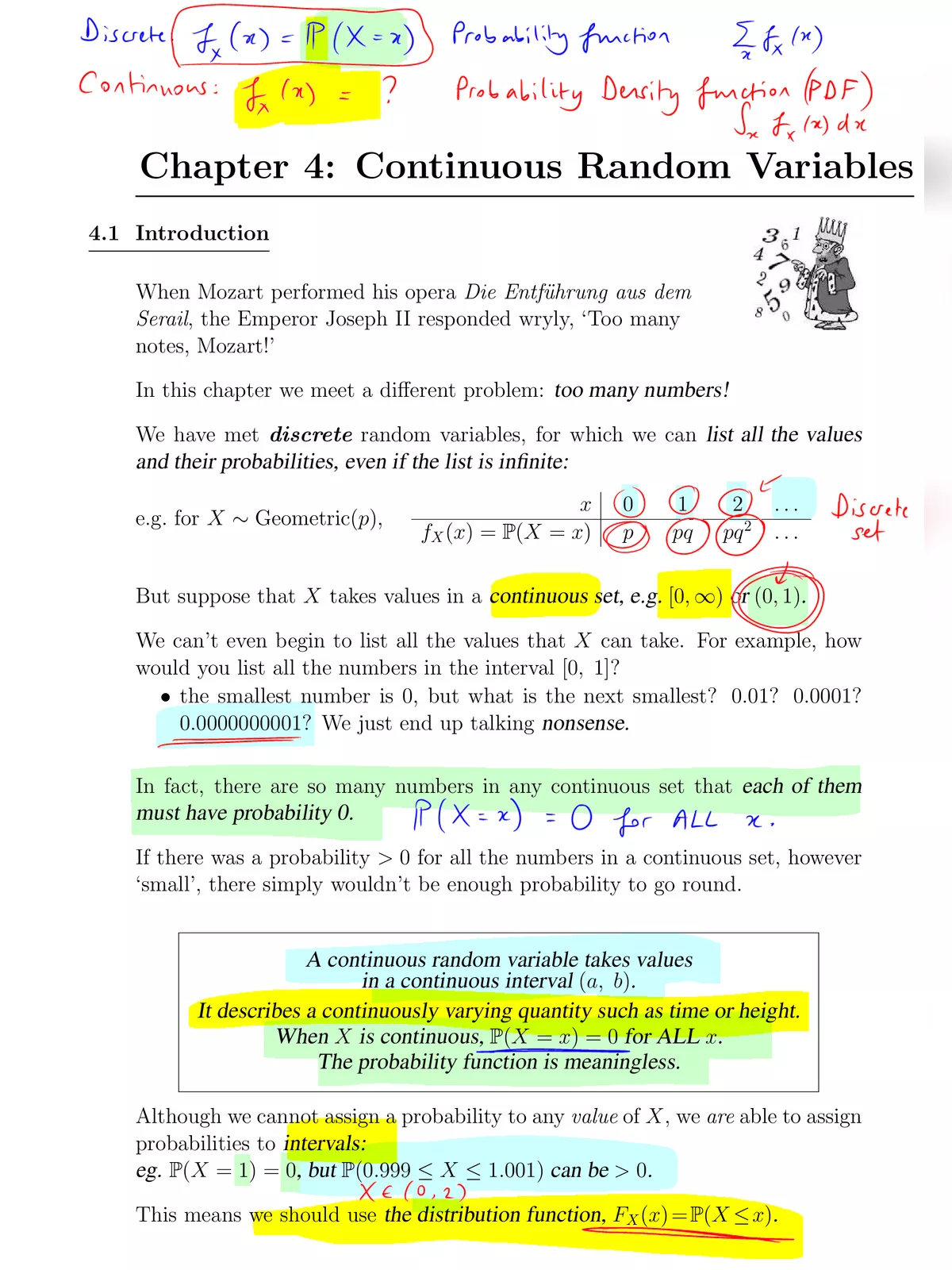
A continuous random variable X is defined in statistics as a variable where P(X = x) = 0 for every value of x. This means that X can take on an endless range of values, which makes it different from a discrete random variable. In a discrete random variable, P(X = x) > 0 for only a few specific values that are finite or countably infinite.
Understanding Continuous Random Variables
When we say that X is a continuous random variable, we open our minds to countless possibilities for linked random variables. For example, if we have Y = g(X), where g is a function of X, then Y also becomes a random variable. This introduces the essential concepts of cumulative distribution function (CDF) and probability density function (PDF).
Finding the PDF from the CDF
If you want to find the PDF of Y, it’s often simpler if we start with its CDF. To get the PDF, we take the derivative of the CDF. However, it’s very important to confirm that the CDF is continuous first before we do this differentiation. Keep in mind that sometimes a function of a continuous random variable can lead to a non-continuous random variable.
Don’t forget to download the Let X be a Continuous Random Variable With PDF format using the link given below! 📥