Psychrometric Chart - Summary
The psychrometric chart is a vital tool in the industry that helps us understand the connections between dry air, moisture, and energy. If you design or maintain air-conditioning systems in buildings, knowing how to read this chart can make your work much easier. With the psychrometric chart, engineers and technicians can better evaluate psychrometric processes and find effective solutions. This chart is key to understanding how different air supply parameters relate to relative humidity.
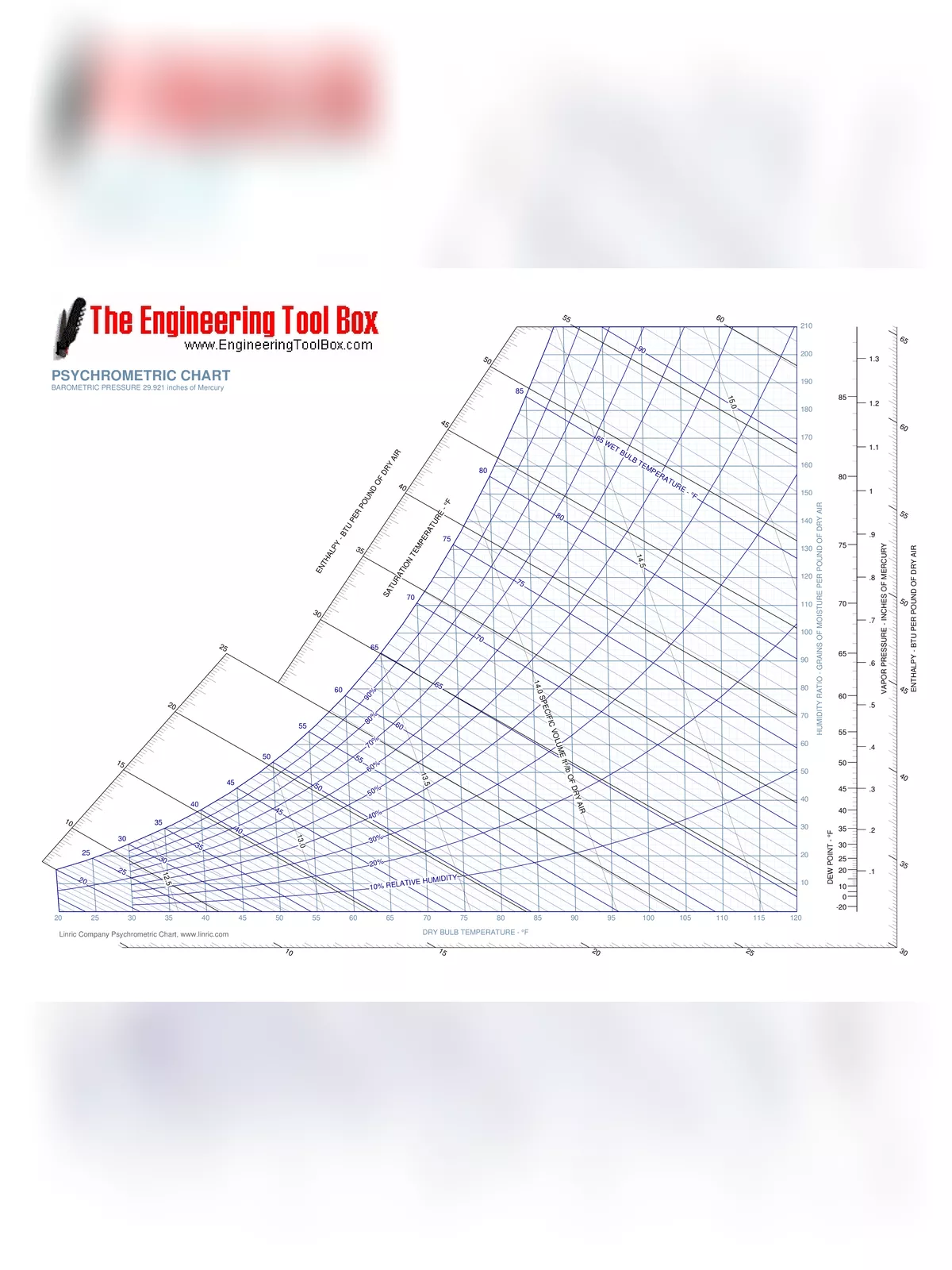
Parts of a Psychrometric Chart
A psychrometric chart consists of eight standard components:
- Temperatures
- Dry Bulb – This is the temperature measurement you see on a thermometer. The psychrometric chart usually displays these temperature ranges:
- Low temperatures from -20 degrees FDB to 50 degrees FDB
- Normal temperatures from 20 degrees FDB to 100 degrees FDB
- High temperatures from 60 degrees FDB to 250 degrees FDB
- Wet Bulb – This is the temperature recorded when a standard thermometer’s sensing bulb is covered with a wet wick and exposed to airflow.
- Dew Point – At this temperature, moisture starts to condense from the air.
- Latent Heat Flow – 60(latent heat of vaporization of water in Btu/lb (970 at sea level))(density of air in lb/ft³)(air flow in ft³/min)(humidity ratio difference in lb water/lb dry air)
- Moisture Content – Also known as humidity ratio, this represents the total weight of water vapor in one pound of dry air.
- Relative Humidity – This term means the percentage of water vapor per pound of dry air compared to how much water vapor the air can hold at its current temperature.
- Vapor Pressure – Measured in inches of mercury, vapor pressure indicates the pressure water vapor exerts in the air.
- Standard Air Dot – This dot represents standard air, typically at 70 degrees Fahrenheit with 54% relative humidity and 60 gr/lb of specific humidity.
- Specific Volume & Density – Specific volume is given in cubic feet per pound, showing how much space air occupies per pound.
- Enthalpy – This indicates heat energy, measured in Btu (British thermal unit) per pound of dry air.
- Sensible Heat Ratio – This ratio is calculated by dividing the total sensible heat flow by the total heat flow.
- Sensible Heat Flow – 60(specific heat of air in Btu/lb ºF (0.24 at 72ºF))(density of air in lb/ft³)(air flow in ft³/min)(| supply air temperature – conditioned room temperature |)
How to Read the Psychrometric Chart
Reading a psychrometric chart is simple if you follow these steps:
Step 1: Locate the dry bulb temperature, shown along the bottom axis in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius, and find the matching vertical line for each temperature.
Step 2: Look for the humidity ratio, marked as a mixing ratio on the right vertical axis. Humidity ratio can be expressed in grains of moisture per pound of dry air or grams of moisture per kilogram of dry air.
Step 3: Identify the left-most curved line, which indicates the saturation curve at 100% relative humidity.
Step 4: Spot the inner curved lines that represent different levels of relative humidity percentages.
Step 5: Find the dew point, marked by a vertical line on the right side of the chart, which extends horizontally across the chart.
Step 6: On the opposite side of the dew point’s vertical line, you will see the vapor pressure scale, also displayed as horizontal lines across the chart.
Step 7: Check the chart’s outer sides for scales that represent enthalpy. Use a ruler to align these scales across the chart.
Step 8: Locate the second set of diagonal lines showing wet bulb temperatures. While they are close to the enthalpy lines, they are not perfectly parallel.
You can easily download the Psychrometric Chart PDF using the link provided below for your reference and further reading. Enjoy using the psychrometric chart in your air-conditioning tasks! 📊