List of All Geometry Formulas - Summary
Geometry is an important branch of mathematics that deals with shapes, sizes, figures, and the space around us. It helps us understand points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids in a clear way. From basic shapes like triangles and circles to 3D objects like cubes and spheres, geometry explains how to measure and calculate different properties such as area, perimeter, surface area, and volume.
Formulas in geometry make solving problems easier and faster. They give us ready-made equations to find measurements without long calculations. Whether it is finding the area of a rectangle, the circumference of a circle, or the volume of a cylinder, geometry formulas save time and help us in both studies and real-life situations like construction, design, and engineering.
List of All Geometry Formulas for Classes 6 to 12th
| SHAPES | FORMULAS |
|---|---|
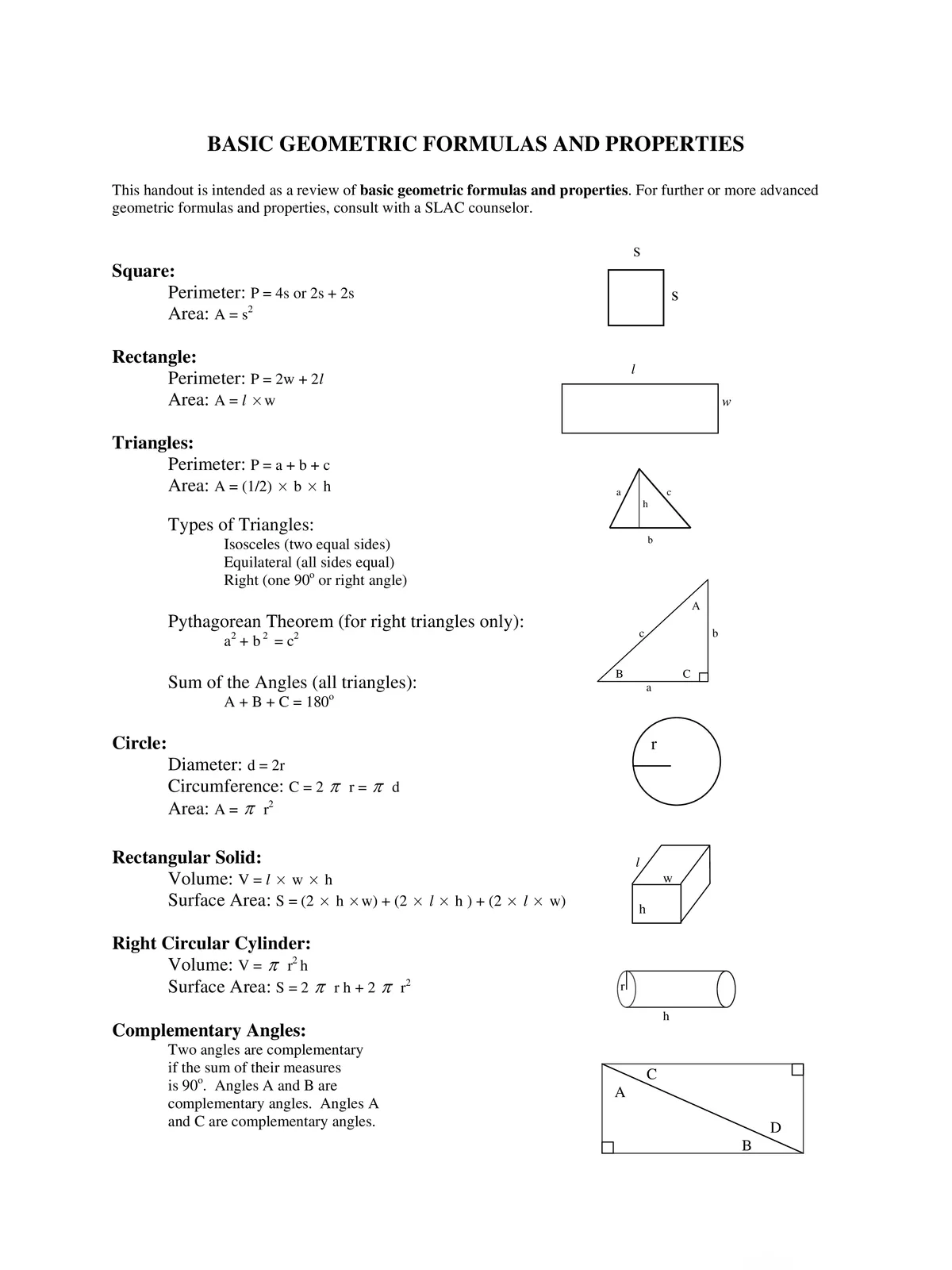
| 1. Right Triangle | Pythagoras Theorem: a2 + b2 = c2 Area = ½ ab Perimeter = a + b + √(a2 + b2) Where, c = hypotenuse of a triangle a = altitude of a triangle b = base of a triangle |
| 2. Triangle | Perimeter, P = a + b + c Area, A = ½ bh Height, h = 2(A/b) Where, a,b,c are the sides of a triangle. |
| 3. Rectangle | Perimeter = 2(l + w) Area = lw Diagonal, d = √(l2 + w2) Where, l = length of a rectangle w = width of a rectangle |
| 4.Parallelogram | Perimeter, P = 2(a + b) Area, A = bh Height, h = A/b Base, b = A/h Where, a and b are the sides of a parallelogram h = height of a parallelogram |
| 5. Trapezium | Area, A = ½(a + b)h Height, h = 2A/(a + b) Base, b = 2(A/h) – a Where, a and b are the parallel sides h = distance between two parallel sides |
| 6. Circle | Circumference = 2πr Area = πr2 Diameter = 2r Where, r = radius of a circle |
| 7. Square | Perimeter, P = 4a Area, A = a2 Diagonal, d = a√2 Side, a = √A = d/2√2 Where, a = side of a square |
| 8. Arc | Arc Length, L = rθ Area, A = ½r2θ Here, θ is the central angle is radians. Where, r = radius |
| 9. Cube | Area, A = 6a2 Volume, V = a3 Edge, a = V⅓ Space diagonal = a√3 Where, a = side of a cube |
| 10. Cuboid | Surface Area, A = 2(lb + bh + hl) Volume, V = lbh Space diagonal, d = √( l2 + b2 +h2) Where, l= length b= breath h= height |
| 11. Cylinder | Total Surface Area, A = 2πrh + 2πr2 Curved Surface Area, Ac = 2πrh Volume, V = πr2h Base Area, Ab = πr2 Radius, r = √(V/πh) Where, r= radius of a cylinder h= height of a cylinder |
| 12. Cone | Total Surface Area, A = πr(r+l) = πr[r+√(h2+r2)] Curved Surface Area, Ac = πrl Volume, V = ⅓πr2h Slant Height, l = √(h2+r2) Base Area, Ab = πr2 Where, r= radius of a cone h= height of a cone l = slant height |
| 13. Sphere | Surface Area, A = 4πr2 Volume, V = ⁴⁄₃πr3 Diameter = 2r Where, r= radius of a sphere |